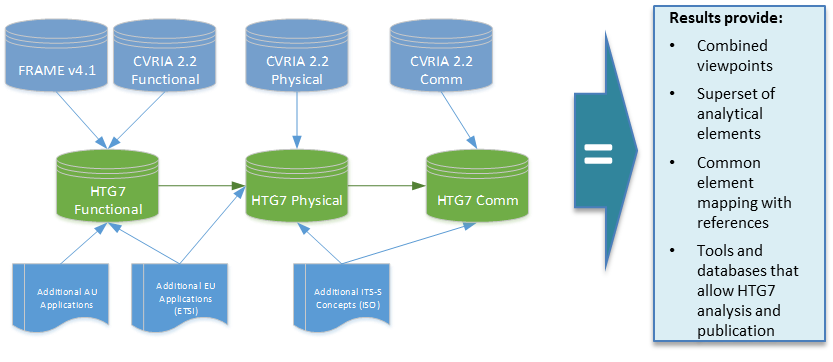
Architecture
There are five major sources of C-ITS content included in the HTG7 architecture:
- The CVRIA, which includes four viewpoints: enterprise, physical, functional and communications, specified in a form compatible with ISO 42010: Systems and Software Definition: Architecture Description.
- C-ITS components of FRAME; FRAME has one viewpoint, the functional, which is similar in form to the CVRIA’s functional.
- C-ITS components of the Australian National ITS Architecture which is based on FRAME, but has some ancillary material related to communications.
- ISO 21217 and related standards information that is specific to C-ITS information flows and functions. These standards are focused on functionality, though the linkage between physical and functional is often straightforward and the detail regarding communications technology is relateable to the CVRIA material.
- ETSI Day 1 applications that are not already in CVRIA or FRAME; these parallel CVRIA’s applications, which are expressions of the physical view.
Based on this understanding of the source material, the HTG7 architecture team developed the Harmonized Architecture for Reference of Technical Standards (HARTS). HARTS is an integrated reference architecture; it integrates architecture of various sources by linking common elements, using as basis for linkage the architecture artifacts most appropriate for the given source. Since the linkage between architectures varied based on the source material, the method of integration varied.